Acute Compartment Syndrome of the Hand in a 14-Month-Old Child: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.38179/ijcr.v2i1.50Keywords:
Acute compartment syndrome, Hand, Trauma, Pediatric, Fasciotomy, Case reportAbstract
Background: Compartment syndrome is a well-known entity, but it is rare in the pediatric population, and its diagnosis is quite challenging. We report a case of an acute compartment syndrome (ACS) of the hand, developed after a crushing trauma, in a 14-month-old boy.
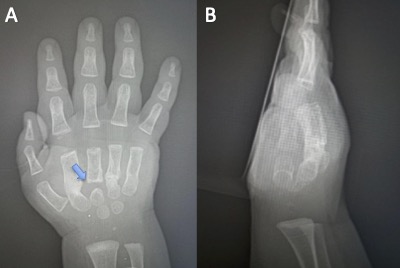
Case Report: A 14-month-old boy presented to the Emergency Department following a crushing trauma to his right hand. The patient had a progressive swelling of the right hand and agitation. On physical examination, the right hand was tense, swollen, with areas of skin necrosis and blisters, along with increased agitation upon palpation. Laboratory tests revealed elevated white blood cells, creatinine kinase, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Radiographic imaging showed deviated diaphyseal fractures in the second, third, fourth, and fifth metacarpals. A diagnosis of ACS of the hand was made. After draining the blisters, multiple fasciotomies were carried out to all 11 compartments of the hand. The metacarpal fractures were managed conservatively with a wrist splint for one month. A clinical and radiological follow-up after 7 months showed a complete functional recovery of the right hand and consolidation of the 2nd, 4th, and 5th metacarpal fractures, while the 3rd metacarpal fracture showed pseudoarthrosis.
Conclusion: Compartment syndrome of the hand in children is a rare condition, and its clinical picture may differ from that in adults, leading to a misdiagnosis or late diagnosis in many cases. Our case emphasizes the importance of a careful clinical evaluation in children post-trauma to diagnose such a condition.
References
Volkman RV. Die ischaemischen muskellahmungen und kontrakturen. Centralblat fur hirurgie. 1881;8:801-3.
Reichman EF. Compartment Syndrome of the Hand: A Little Thought about Diagnosis. Case Rep Emerg Med. 2016;2016:2907067. PMID: 27293917. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2907067
Grottkau BE, Epps HR, Di Scala C. Compartment syndrome in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40(4):678-682. PMID: 15852278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2004.12.007
Broom A et al. Compartment syndrome in infants and toddlers. J Child Orthop. 2016;10(5):453-460. PMID: 27538943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-016-0766-0
Noonan K, McCarthy J. Compartment Syndromes in the Pediatric Patient. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2010;30(Supplement 2):S96-S101. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181d07118
Malik SS, Uppal H, Sinha A, Malik SS, Katam K, Srinivasan K. Acute paediatric compartment syndrome of the hand caused by hereditary angiooedema. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2011;93(7):e138-e140. https://doi.org/10.1308/147870811x602159
Venditto C, Jager Z, LoGiudice J, Matloub H. Pediatric Hereditary Angioedema as a Cause of Acute Compartment Syndrome of the Hand and Forearm: A Case Report. Hand (N Y). 2017;12(3):NP46-NP50. PMID: 28453344. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558944716668830
Hak DJ. Acute Compartment Syndrome in Children. In: Mauffrey C, Hak DJ, Martin III MP, eds. Compartment Syndrome: A Guide to Diagnosis and Management. Cham (CH): Springer; September 3, 2019.125-132. PMID: 32091730. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22331-1_13
Raza H, Mahapatra A. Acute compartment syndrome in orthopedics: causes, diagnosis, and management. Adv Orthop. 2015;2015:543412. PMID: 25688303. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/543412
Erdös J, Dlaska C, Szatmary P, Humenberger M, Vécsei V, Hajdu S. Acute compartment syndrome in children: a case series in 24 patients and review of the literature. Int Orthop. 2011;35(4):569-575. PMID: 20401657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-010-1016-6
Lin JS, Samora JB. Pediatric acute compartment syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2020;29(1):90-96. PMID: 30688754. https://doi.org/10.1097/bpb.0000000000000593
Bae DS, Kadiyala RK, Waters PM. Acute compartment syndrome in children: contemporary diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001;21(5):680-688. PMID: 11521042. https://doi.org/10.1097/01241398-200109000-00025
Gresh M. Compartment Syndrome in the Pediatric Patient. Pediatr Rev. 2017;38(12):560-565. PMID: 29196511. https://doi.org/10.1542/pir.2016-0114
Giannotti G et al. the utility of near infrared spec-troscopy (NIR) in the diagnosis of lower extremity compartment syndrome. The Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical Care. 1999;47(1):218. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00005373-199907000-00090
Marmor M, Charlu J, Knox R, Curtis W, Hoogervorst P, Herfat S. Use of standard musculoskeletal ultrasound to determine the need for fasciotomy in an elevated muscle compartment pressure cadaver leg model. Injury. 2019;50(3):627-632. PMID: 30745127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2019.01.015
Lim KBL, Laine T, Chooi JY, Lye WK, Lee BJY, Narayanan UG. Early morbidity associated with fasciotomies for acute compartment syndrome in children. J Child Orthop. 2018;12(5):480-487. PMID: 30294372. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.12.180049
Finkelstein JA, Hunter GA, Hu RW. Lower limb compartment syndrome: course after delayed fasciotomy. J Trauma. 1996;40(3):342-344. PMID: 8601846. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005373-199603000-00002
Whitesides TE, Heckman MM. Acute Compartment Syndrome: Update on Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1996;4(4):209-218. PMID: 10795056. https://doi.org/10.5435/00124635-199607000-00005
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 International Journal of Clinical Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.