Lyme Borreliosis Associated with Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.38179/ijcr.v2i1.68Keywords:
Sensorineural hearing loss, Lyme borreliosis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Neuroborreliosis, Case reportAbstract
Background: Lyme borreliosis is a tick-borne infection caused by Borrelia species. It has a geographic distribution that makes it more frequent in certain regions like like North America and Europe. It manifests in a wide range of symptoms but is often under-investigated in patients presenting with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL).
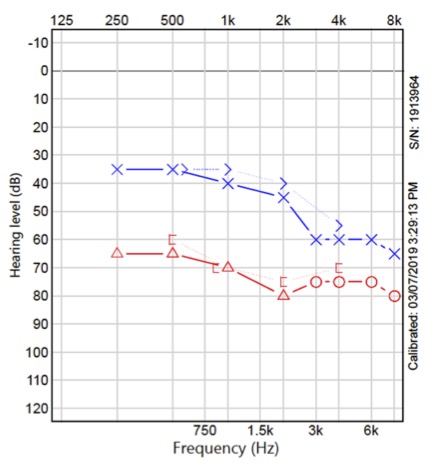
Case Report: In this report, we describe a case presenting with SNHL as a manifestation of neuroborreliosis in a female adult patient suffering from Lyme disease, with multiple metachronous symptoms, including arthritis and seizures. Lyme borreliosis (LB) was clinically diagnosed and supported by positive serologic tests, along with Babesiosis. The patient was treated with intravenous (IV) ceftriaxone and azithromycin, in addition to oral atovaquone. Improvement after 4 weeks of IV ceftriaxone was noted in all aspects, including SNHL and arthritis.
Conclusion: LB is a possible, but rare, etiology of hearing impairment. It has been documented that if treatment is initiated early, improvement and even complete recovery are possible. Hence, in a patient presenting with SNHL and a high index of suspicion for LB, assessment for LB is warranted.
References
US National Institute for Deafness and Communication Disorders [Internet]. Available from: www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/sudden-deafness
Chandrasekhar S. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update) [Internet]. Otolaryngol Head and Neck Surg; 2019. Available from: https://www.entnet.org/content/clinical-practice-guideline-sudden-hearing-loss-update-2019
Alexander TH, Harris JP. Incidence of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol. 2013;34(9):1586-1589. PMID: 24232060. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000000222
Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(5):1011-1021. PMID: 20422698. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20873
Slattery WH, Fisher LM, Iqbal Z, Liu N. Oral steroid regimens for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;132(1):5-10. PMID: 15632902.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2004.09.072
Espiney Amaro C, Montalvão P, Huins C, Saraiva J. Lyme disease: sudden hearing loss as the sole presentation. J Laryngol Otol. 2015;129(2):183-186. PMID: 25619547. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215114003417
Lorenzi MC, Bittar RS, Pedalini ME, et al. Sudden deafness and Lyme disease. Laryngoscope. 2003;113(2):312-315. PMID: 12567088. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200302000-00021
Aydin L, Bakirci S. Geographical distribution of ticks in Turkey. Parasitol Res. 2007;101 Suppl 2:S163-S166. PMID: 17823820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0694-5
Fisher JB, Curtis CE. An unexpected case of Lyme disease in a soldier serving in northern Iraq. Mil Med. 2010;175(5):367-369. PMID: 20486511. https://doi.org/10.7205/milmed-d-09-00079
Önal U, Aytaç Erdem H, Uyan Önal A, Reşat Sipahi O. Systematic review of Lyme disease in Turkey. Trop Doct. 2019;49(3):165-170. PMID: 31018773. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049475519843387
Steere AC, Strle F, Wormser GP, et al. Lyme borreliosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16090. PMID: 27976670. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.90
Koedel U, Pfister HW. Lyme neuroborreliosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017;30(1):101-107. PMID: 27820708. https://doi.org/10.1097/qco.0000000000000332
Hu LT. In the clinic. Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(3):ITC2-2-ITC2-16. PMID: 22868858. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-157-3-201208070-01002
Aguero-Rosenfeld ME, Wang G, Schwartz I, Wormser GP. Diagnosis of lyme borreliosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18(3):484-509. PMID: 16020686. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.18.3.484-509.2005
Bakker R, Aarts MC, van der Heijden GJ, Rovers MM. No evidence for the diagnostic value of Borrelia serology in patients with sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;146(4):539-543. PMID: 22394551. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599811432535
Nadelman RB, Luger SW, Frank E, Wisniewski M, et al. Comparison of cefuroxime axetil and doxycycline in the treatment of early Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117(4):273-280. PMID: 1637021. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-117-4-273
Jozefowicz-Korczynska M, Zamyslowska-Szmytke E, Piekarska A, Rosiak O. Vertigo and Severe Balance Instability as Symptoms of Lyme Disease-Literature Review and Case Report. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1172. PMID: 31798513. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.01172
Halperin JJ, Shapiro ED, Logigian E, et al. Practice parameter: treatment of nervous system Lyme disease (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2007;69(1):91-102. PMID: 17522387. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000265517.66976.28
Wormser GP, Dattwyler RJ, Shapiro ED, et al. The clinical assessment, treatment, and prevention of lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43(9):1089-1134. PMID: 17029130. https://doi.org/10.1086/508667
Wormser GP, McKenna D, Scavarda C, et al. Co-infections in Persons with Early Lyme Disease, New York, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25(4):748-752. PMID: 30882316. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2504.181509
Peeters N, van der Kolk BY, Thijsen SF, Colnot DR. Lyme disease associated with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: case report and literature review. Otol Neurotol. 2013;34(5):832-837. PMID: 23303170. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0b013e31827c9f93
Bertholon P, Cazorla C, Carricajo A, Oletski A, Laurent B. Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss and cerebellar ataxia in the case of late stage Lyme disease. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;78(6):124. PMID: 23306581. https://doi.org/10.5935/1808-8694.20120046
Vos FI, Merkus P, van Nieuwkerk EB, Hensen EF. Rare cause of bilateral sudden deafness. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016216004. PMID: 28049117. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2016-216004
Uhde M, Ajamian M, Li X, Wormser GP, Marques A, Alaedini A. Expression of C-Reactive Protein and Serum Amyloid A in Early to Late Manifestations of Lyme Disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63(11):1399-1404. PMID: 27585799. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciw599
Waddell LA, Greig J, Mascarenhas M, Harding S, Lindsay R, Ogden N. The Accuracy of Diagnostic Tests for Lyme Disease in Humans, A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of North American Research. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0168613. PMID: 28002488. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0168613
Liveris D, Schwartz I, Bittker S, et al. Improving the yield of blood cultures from patients with early Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49(6):2166-2168. PMID: 21490189.https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.00350-11
Henningsson AJ, Christiansson M, Tjernberg I, Löfgren S, Matussek A. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme neuroborreliosis: a comparison of three CSF anti-Borrelia antibody assays. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;33(5):797-803. PMID: 24263552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-2014-6
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Recommendations for test performance and in-terpretation from the Second National Conference on Serologic Diagnosis of Lyme Disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1995;44(31):590–1.
Dressler F, Whalen JA, Reinhardt BN, Steere AC. Western blotting in the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1993;167(2):392-400. PMID: 8380611. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/167.2.392
Hammers-Berggren S, Hansen K, Lebech AM, Karlsson M. Borrelia burgdorferi-specific intrathecal antibody production in neuroborreliosis: a follow-up study. Neurology. 1993;43(1):169-175. PMID: 8423881. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.43.1_part_1.169
Steere AC, McHugh G, Damle N, Sikand VK. Prospective study of serologic tests for lyme disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(2):188-195. PMID: 18532885. https://doi.org/10.1086/589242
Richardson H, Birchall JP, Hill J, McMaster T. Should we routinely screen for Lyme disease in patients with asymmetrical hearing loss?. Br J Audiol. 1994;28(2):59-61. PMID: 7841889. https://doi.org/10.3109/03005369409077915
Walther LE, Hentschel H, Oehme A, et al. [Lyme disease--a reason for sudden sensorineural hearing loss and vestibular neuronitis?]. Laryngorhinootologie. 2003;82(4):249-257. PMID: 12717599. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-38938
Estrada-Peña A, Cutler S, Potkonjak A, et al. An updated meta-analysis of the distribution and prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. in ticks in Europe. Int J Health Geogr. 2018;17(1):41. PMID: 30514310. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12942-018-0163-7
Maniu A, Damian L. Rapid progressive bilateral hearing loss due to granulomatous otitis media in Lyme disease. Am J Otolaryngol. 2013;34(3):245-247. PMID: 23313123.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2012.11.009
Schattner A, Halperin D, Wolf D, Zimhony O. Enteroviruses and sudden deafness. CMAJ. 2003;168(11):1421-1423. PMID: 12771071.
Park A, Doutre S, Schleiss MR, Shoup A. All Cytomegalovirus-infected Children Need Hearing and Neurologic Follow-up. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;70(1):173. PMID: 31090913. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciz399
Eddleston M, Peacock S, Juniper M, Warrell DA. Severe cytomegalovirus infection in immunocompetent patients. Clin Infect Dis. 1997 Jan;24(1):52-6. PMID: 8994755. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinids/24.1.52
Crouch AE, Andaloro C. Ramsay Hunt Syndrome. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; September 27, 2020.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk557409/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Lyme disease--United States, 2003-2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007;56(23):573-576. PMID: 17568368.
Luft BJ, Dattwyler RJ, Johnson RC, et al. Azithromycin compared with amoxicillin in the treatment of erythema migrans. A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124(9):785-791. PMID: 8610947. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-124-9-199605010-00002
Sanchez E, Vannier E, Wormser GP, Hu LT. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Lyme Disease, Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, and Babesiosis: A Review. JAMA. 2016;315(16):1767-1777. PMID: 27115378.https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.2884
Halperin JJ. Diagnosis and management of Lyme neuroborreliosis. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2018;16(1):5-11. PMID: 29278020.https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2018.1417836
Quinn SJ, Boucher BJ, Booth JB. Reversible sensorineural hearing loss in Lyme disease. J Laryngol Otol. 1997;111(6):562-564. PMID: 9231093. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215100137910
Mehler K, Emmel M, Petereit HF, et al. [Sensorineural loss of hearing in lower registers as the main symptom of Lyme disease]. HNO. 2007;55(12):961-963. PMID: 17103202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00106-006-1490-8
Huda S, Wieshmann UC. Protracted neuroborreliosis--an unusual cause of encephalomyelitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2012;2012:bcr1120115206. PMID: 22665558.https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr.11.2011.5206
Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai Do BS, Schwartz SR, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update) Executive Summary. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;161(2):195-210. PMID: 31369349.https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599819859883
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 International Journal of Clinical Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.